Hydrocolloid dressings
Hydrocolloid adhesive dressings from leading brands Biatain, Comfeel and more.
Browse
Popular products
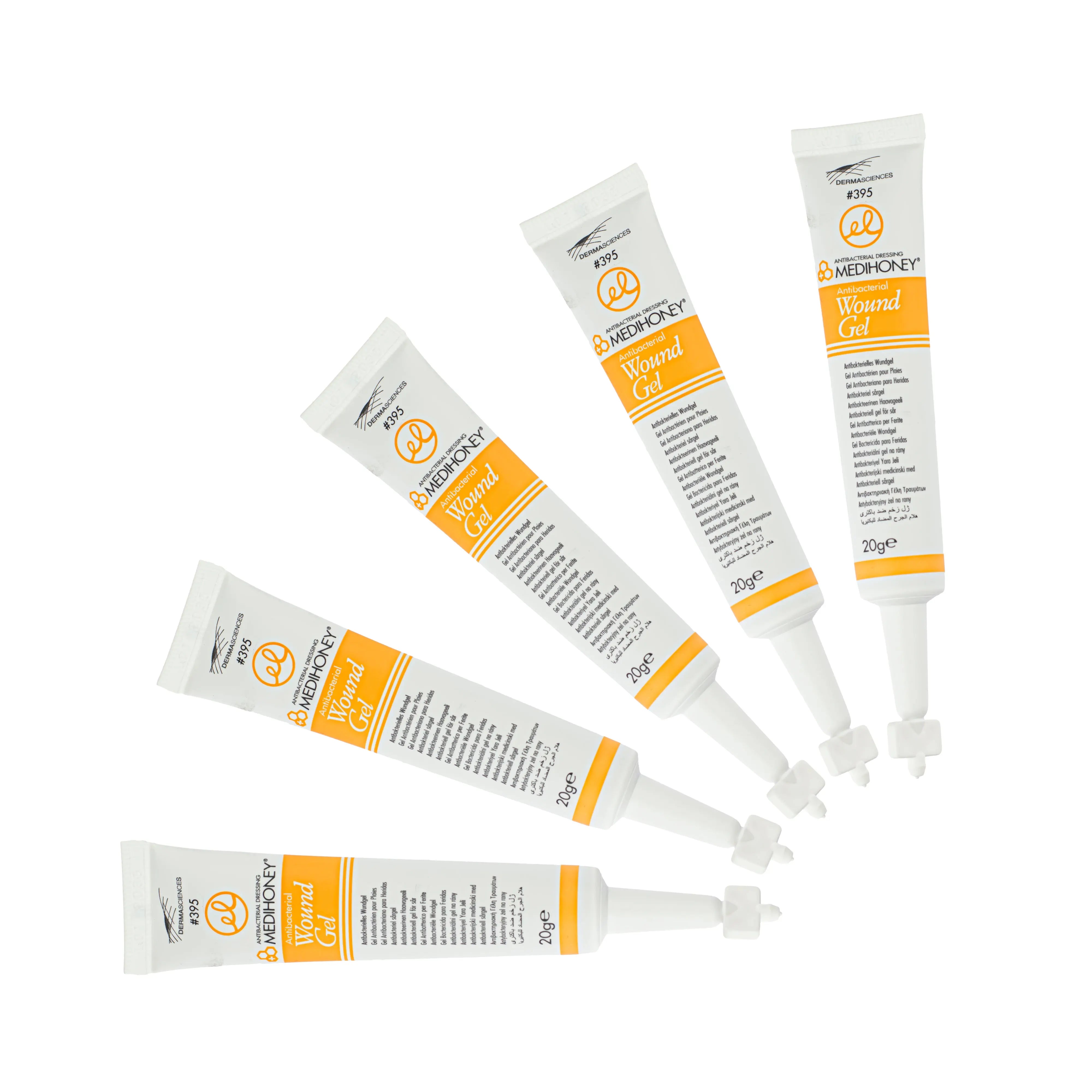

MediHoney
MediHoney Antibacterial Wound Gel - Active Leptospermum Manuka Honey (10g or 20g) (x5 or 20)

MediHoney
MediHoney Antibacterial Apinate Dressing - Active Leptospermum Manuka Honey (10cm x 10cm) (x5)

MediHoney
MediHoney Antibacterial Apinate Rope - Active Leptospermum Manuka Honey (1.9cm x 30cm) ( x5)
Resources